|
|
|
Centrale téléphonique ALAW® (iPBX)
- Fonctionalités en bref
- Architecture
- Fonctionalités en détails
- Bénéfice de la téléphonie sur IP
 Bénéfice de la téléphonie sur IP Bénéfice de la téléphonie sur IP
 In Brief In Brief
The new IP Telephony paradigm results from the convergence of traditional Telecommunication with the computer and Internet worlds.
IP Telephony provides enhanced telephony PBX functionalities at costs far below traditional telephony PBX, and add on top of it features traditional telephony will never support, like Unified Messaging.
IP Telephony also provides new communication path and services, like Free Internet calls of high quality, encrypted communications, or worldwide accessibility as if you were at office
retour au début de la page
 Facts about legacy telephony networks Facts about legacy telephony networks
-
Stable and mature
-
Telecom World
-
Really good for voice, poor for data (Modem 56Kbps asymmetric max)
- Many alternative providers Carrier Preselection - but still a closed world
-
Circuit oriented: physical on local loop and virtual (SVC) in Telco core
-
Telco hardware is manufacturer specific, proprietary
-
Telco's have their own rules, own protocols, own network. (Convergence is already running in Telco core network but remains almost opaque to normal end-user)
-
New functionalities (ex .comfort services) show up at slow pace, and takes time to spread
retour au début de la page  Facts about POTS PBX Facts about POTS PBX
-
Pro
- Well known
- Robust
- Apparent simplicity
- Stability of PSTN
- Many years of experience
-
Contra
retour au début de la page  Facts about data network Facts about data network
Younger than Telco but stable and mature (Data network exists for more than 20 years now)
-
Explosive growth of data networks during late 90's, and especially internet services
-
Realization of the true potential of Internet, followed by a more mature but still sustained growth of services since then
-
Computers processing power keep increasing continuously, while their price keeps lowering.
-
Data network designed at their beginning to offer better bandwidth utilisation than voice network via packet switching
-
Data network first focused on
.data, i.e. non real-time best-effort behaviours but, increase in demand and in processing power lead to multiple Qos network capabilities, including real-time, delay, and jitter sensitive class of services.
-
Qos with its Diffserv model is only used in case of congestion.
-
Voice is a particular form of data, which is QoS sensitive and require near real-time, packet loss, delay and jitter controlled network.
-
Voice is a kind of data which can be compressed efficiently (codec)
-
Data network are driven by open and shared standards and protocols (RFP, IEEE, IETF, W3C,
)
-
Short time to market for new features
-
Wide variety of existing applications
-
Wide variety of programming interfaces
-
Wide developing workforce
-
OPEN SOURCE : non proprietary, wide community, free, follow standards
retour au début de la page  Convergence Convergence
-
Data and voice convergence is an industry wide phenomenon. Ex : UMTS , Voice over ADSL, Voice over ATM
 Idea beyond the convergence Idea beyond the convergence
Reduce costs by merging the two distinct network infrastructures in one multipurpose network
-
Lower cost of ownership (licences, devices, knowledge,
)
-
Lower cost of advanced functionalities, allow use of those in smaller entities
-
Open voice market to a wider range of manufacturer
-
Increase functionalities development and deployment provided by computer and telephony integration (CTI) : Increase efficiency with customer, offer new services
-
Integrate different way of communication inside a common framework : Unified messaging
retour au début de la page
 Steps towards IP Telephony Steps towards IP Telephony
carry voice from legacy PBX in parallel with high bandwidth data (VoADSL,...)
-
carry voice between legacy PBX via tunnels build on data network (VoIP, VoFR,
)
-
Add native VoIP support to legacy PBX
-
Add native ToIP support to legacy PBX
-
Full IP PBX - OPEN SOURCE ToIP
-
CTI, Unified messaging (IM, Voice2Email,
)
retour au début de la page  Facts about IP PBX Facts about IP PBX
- Pro
- New services towards internal customers
- least cost follow-me
- multiplication of incoming channels on existing telecom circuits
- New services towards external customers
- CRM
- IPCC
- Unified messaging
- IVR
- Inherit of the strongnesses of computer based technologies
- Ubiquity
- Flexibility
- Open architecture (not always)
- Cost effective
- Layered architecture best of bread in each vendor independant
- Flexible
- Future proof
- standard industry components
- Mobility
- Unified Infrastructure
- Unified Messaging
- Multi-vendor Phones support
- Privacy (encryption of voice)
- Remote monitoring, maintenance
- Wide scaleable (Number of users, Number of sites, Number of features)
- Simple to connect
- Teleworking
- + ROI
- Contra
- Reorganisation inside telecom departments of customers
- New Learning curve
- Inherit of the weaknesses of computer based technologies (security, fiability) - requires special care in design and configuration
 Evolution of functionalities vs prices Evolution of functionalities vs prices
- POTS PBX
- MIX POT/IPTEL PBX
- IPTEL PBX
- Advanced IPTEL on proprietary protocols
- Open IPTEL
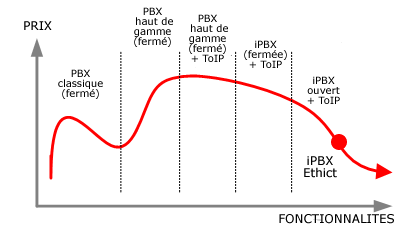
- PBX : Centrale téléphonique classique
- iPBX : Centrale téléphonique "nouvelle génération", serveur informatique
- VoIP : Voix sur IP - transport de la voix sur le réseau de donnée, plus besoin de cablages séparés pour le réseau téléphonique et le réseau de donnée
- ToIP : Téléphonie sur IP = VoIP + iPBX ou VoIP + adapteur + PBX
- PBX fermé : PBX "propritéraire", c.à.d dont seul le fabricant détient les plans et programmes
- iPBX ouvert : iPBX non propritaire = dont les plans et programmes sont librement accessibles et modifiables (ex: Linux)
|
|

